Heat resistant insulated electrical connectors are essential components in electrical systems where elevated temperatures could compromise standard wiring connections. They combine insulation with materials that can withstand high temperatures, making them ideal for automotive engines, industrial machinery, and high-power electronic applications. To help users understand their purpose and functionality, here are several frequently asked questions about these connectors.
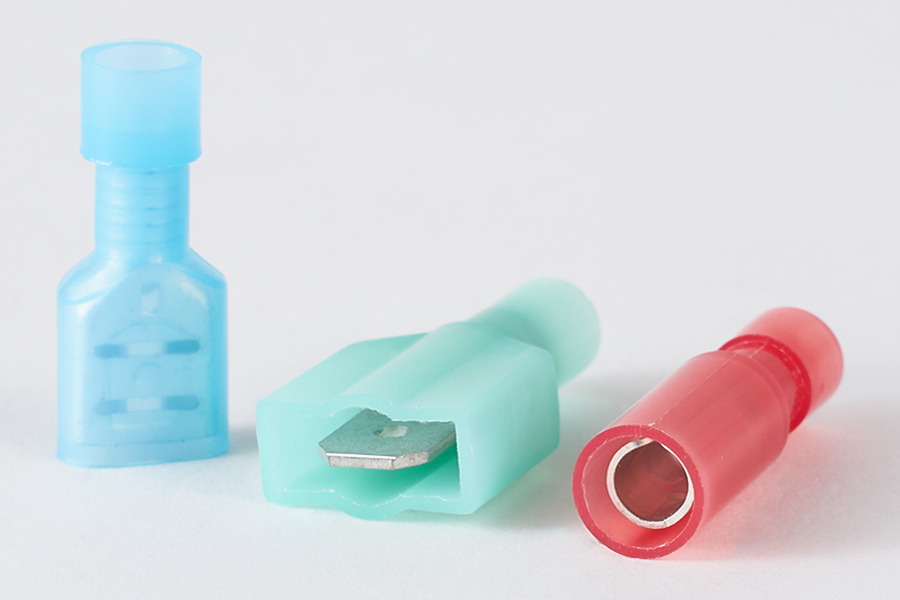

A heat resistant insulated connector is designed with materials capable of enduring higher temperatures than standard connectors. The metal portion is typically made of copper, brass, or tin-plated alloys, which maintain electrical conductivity under heat stress. The insulation is made from specialized polymers such as nylon, PTFE, or silicone, which resist melting, deformation, and degradation at high temperatures. The combination ensures both electrical continuity and mechanical stability, even in conditions.
What are the benefits of using heat resistant insulated connectors?
1. Enhanced Safety and Fire Prevention: This is the primary benefit. Heat-resistant insulation, often made from materials like silicone, fiberglass, or special cross-linked polymers, can withstand high temperatures without melting, degrading, or catching fire. This contains electrical arcs or short circuits within the connector, preventing them from igniting surrounding materials.
2. Superior Reliability in High-Temperature Environments: In applications like automotive engine bays, industrial machinery, appliance internal wiring, and lighting fixtures, temperatures can soar. Standard insulation (like PVC) can melt, become brittle, and crack, exposing live conductors. Heat-resistant connectors maintain their integrity, ensuring a continuous, safe connection and preventing unexpected failures.
3. Protection from External Heat Sources: Connectors are often routed near hot components like exhaust manifolds, boilers, or ovens. Heat-resistant insulation acts as a protective barrier, preventing the external heat from damaging the internal metal terminal and the wire crimp, which could otherwise lead to a rise in resistance and potential failure.
4. Prevention of Insulation Shrinkback: When subjected to heat, some insulating materials can shrink back from the metal terminal, exposing the bare wire. Heat-resistant materials are specifically engineered to resist this, maintaining full coverage and preventing accidental short circuits.
5. Improved Mechanical Durability: The materials used for heat resistance often have excellent flexibility and resistance to chemicals, oils, and abrasion. This makes the overall connection point more robust, capable of withstanding harsh conditions beyond just high heat, such as in industrial or automotive applications.
Where are heat resistant insulated connectors typically used?
Applications include automotive wiring, especially near engines and exhaust systems; industrial control panels with high-power components; heating appliances such as ovens; and renewable energy systems, where solar inverters may reach elevated temperatures. Essentially, any environment where standard insulation might fail due to heat is a candidate for these specialized connectors.
How do you install them correctly?
Installation involves selecting the right connector for the wire gauge and crimping it securely with a compatible tool. Heat resistant connectors are often color-coded by wire size, similar to standard insulated connectors. After crimping, it is crucial to inspect the connection for firmness and proper insulation coverage. Some applications may also require a heat-resistant sleeve or shrink tubing for additional protection. Proper installation ensures safety, performance, and longevity.
Heat resistant insulated connectors are crucial for high-temperature applications, providing safety, reliability, and durability. Understanding their materials, benefits, and installation ensures that electrical systems can withstand heat without compromising performance or safety.
Electrical Wire Crimp Connectors
Electrical wire crimp connectors are widely used in various industries due to their reliability, ease of installation, and mechanical stability. A crimp connector allows an electrical conductor to be mechanically pressed into a connector terminal, providing a secure and permanent connection. These connectors are used in automotive wiring, household appliances, industrial machinery, and electronic devices.
What types of wire crimp connectors are available?
Wire crimp connectors come in several designs, each suited for specific applications:
Ring terminals: Designed to be placed around a screw or bolt, providing a secure mechanical connection.
Spade or fork terminals: Allow quick attachment and removal without fully removing the fastener.
Butt connectors: Enable end-to-end wire joining, commonly used in splicing applications.
Bullet connectors: Offer a plug-and-socket style connection for wires that may require frequent disconnection.
Quick disconnect terminals: Facilitate tool-free connections for low to moderate current applications.
Each type is available in insulated and non-insulated versions, with insulation typically color-coded to indicate wire gauge compatibility. Insulated connectors provide additional protection against shorts, while non-insulated connectors are often preferred in enclosed or high-density wiring applications.
Why use crimp connectors instead of soldering?
Crimping offers several advantages over soldering. Firstly, it is faster and more consistent, which is important in assembly lines or mass production. Secondly, a properly crimped connection is mechanically stronger than a soldered joint, making it more resistant to vibration and wire fatigue. Thirdly, crimping is safer, as it does not involve hot soldering tools or molten metal, reducing the risk of burns or damage to insulation. While soldering may provide conductivity, crimping provides an effective balance of electrical performance, mechanical integrity, and ease of installation.
How do you ensure a reliable crimp connection?
Reliability depends on selecting the right connector for the wire gauge and using a quality crimping tool designed for that connector type. The wire must be stripped correctly without damaging strands. Insert the stripped conductor fully into the crimp barrel and compress it evenly with the crimping tool until the connector is securely fastened. After crimping, a pull test is recommended to verify that the wire is firmly held. Proper technique ensures that the connection maintains low resistance and mechanical stability over time.
Applications of wire crimp connectors
Wire crimp connectors are used in applications ranging from automotive wiring harnesses to household appliance assembly, industrial equipment, and electronic devices. They are ideal in environments where vibration, mechanical stress, or repeated disconnections occur. Insulated crimp connectors also provide protection against short circuits, making them suitable for exposed or high-density wiring assemblies.
Advantages of crimp connectors
- Time-saving installation compared to soldering.
- Mechanical strength that resists vibration and wire fatigue.
- Consistent electrical performance when installed correctly.
- Versatility in connector types for different applications and wire gauges.
- Safety due to insulated options and tool-assisted crimping.
Both heat resistant insulated electrical connectors and wire crimp connectors play vital roles in modern electrical systems. Heat resistant connectors are crucial for high-temperature environments, providing insulation and mechanical stability to prevent failures or hazards. Wire crimp connectors offer versatility and efficiency in a wide range of applications, delivering reliable connections with minimal installation time.
Understanding the materials, types, benefits, and installation procedures of these connectors ensures that electrical systems are both safe and durable. Using the appropriate connector type for the application—considering factors like temperature, mechanical stress, and wire gauge—optimizes system reliability and reduces maintenance issues.
Together, these components highlight the importance of choosing the right connector for the right application and applying correct installation techniques. With proper knowledge, electricians, engineers, and DIY enthusiasts can ensure efficient, safe, and long-lasting electrical connections in both residential and industrial settings.

 English
English Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch